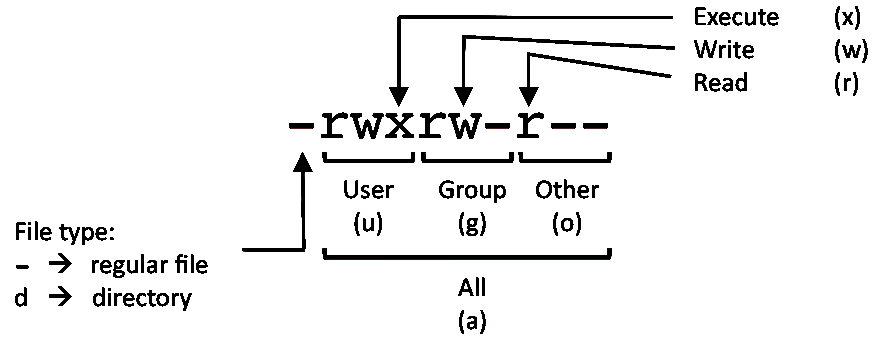
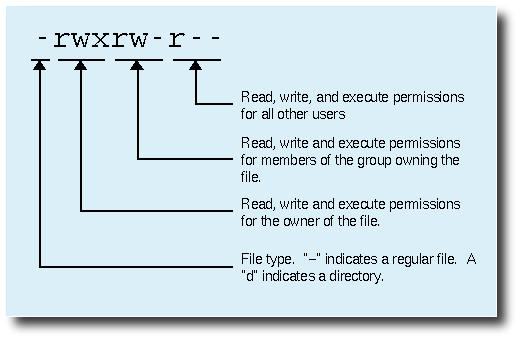
The syntax of the chmod command when using numeric method has the following format chmod OPTIONS NUMBER FILE When using the numeric mode, you can set the permissions for all three user classes (owner, group, and all others) at the same time The NUMBER can be a 3 or 4digits numberChmod means 'change mode' and it changes file or directory mode bits (the way a file can be accessed) You can use chmod in the command line to change file or directory permissions on unix or unixlike systems such as linux or BSDChmod stands for change mode, which changes the file or directory mode bits To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions Following is a sample of ls l command output In this, the 9 characters from 2nd to 10th position represents the
Useradd Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
Chmod command in linux syntax
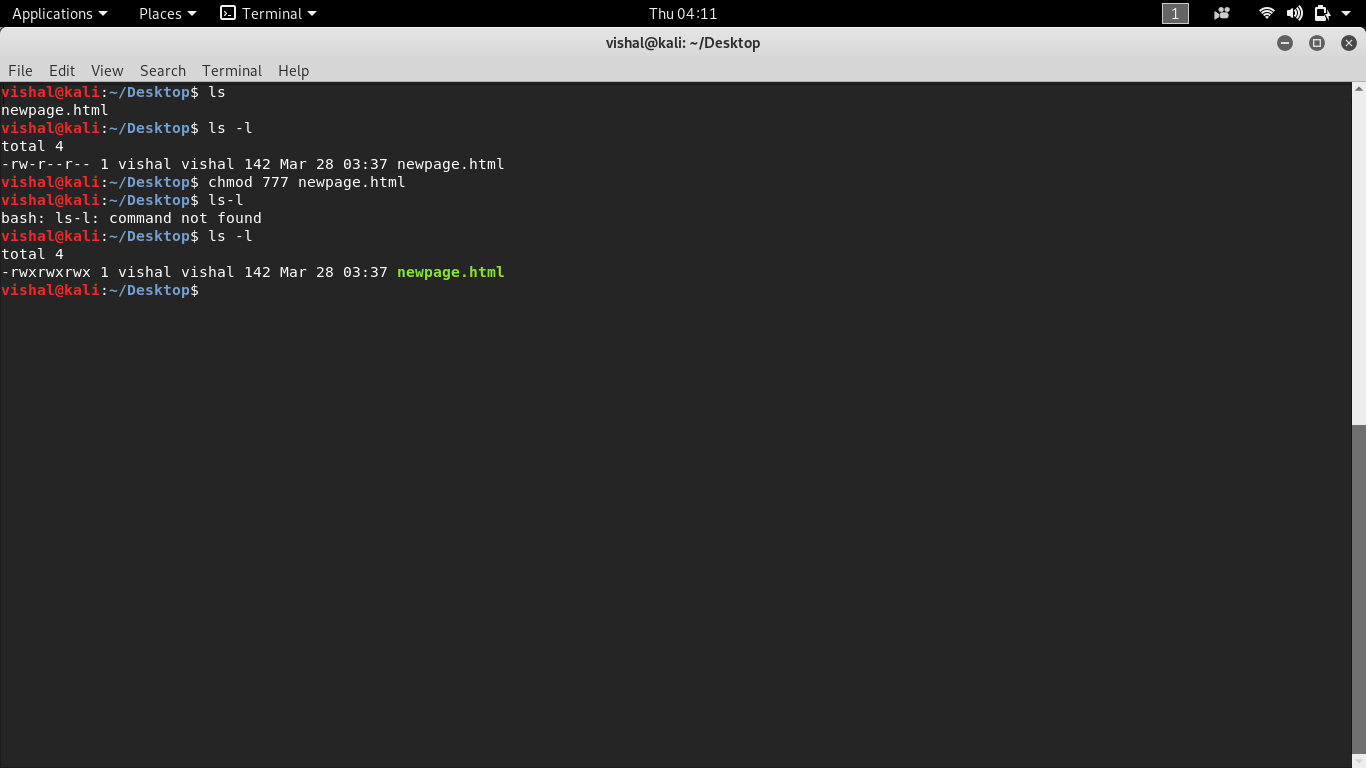
Chmod command in linux syntax- First, open terminal Then use the cd command to go to the directory where the file you want edit is Now use the following command to see the permission granted to the file Ls –l filename Now you just need to use the attributes explained above Use the following example to execute the chmod command in Linux In Linux, you will often need to make use of the chmod command Chmod stands for " Change Mode " and is used to modify the permissions of files and directories in a Linux based system By using this command, we can set the read , write , and execute permissions for all three of the permission groups ( Owner , Group and Other ) in Linux




Linux Commands Chmod
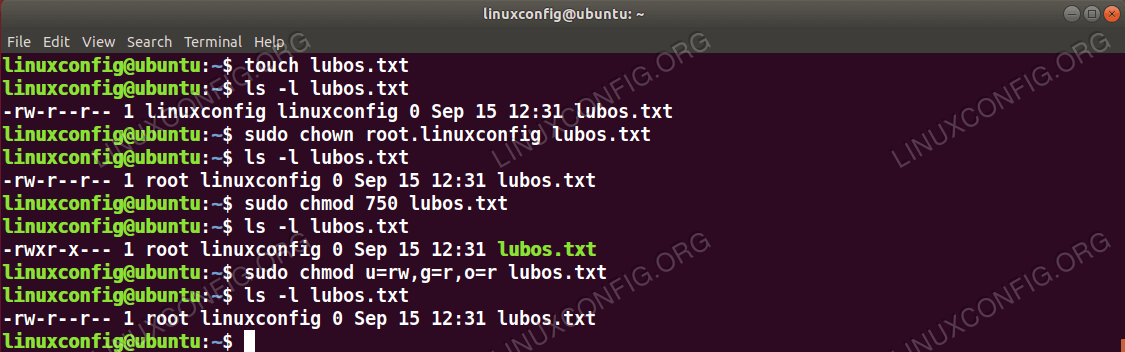
The command CHMOD stands for change mode, and this is used to change the permission of a File or Directory The Command CHOWN stands for Change Owner and this is used to change the ownership of a File or Directory Also Read Linux Tutorial for Beginners && Git Tutorial for BeginnersG stands for group;So the formula for assigning permissions using chmod command is shown below u – User;
The chmod command helps to change Some specific permissions As you noticed that the permissions are set either by using the numeric or the symbolic method We hope that the information provided in this article added value to your knowledge and widened the horizons of your Linux chmod command or "change mode command", and as that name implies, the chmod command is used to change the mode of Unix/Linux files In other words it is used to define the way a file can be accessedThis video explains chmod and chown commandspart 1 https//wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=kzRZVjHatuouser management in linuxhttps//wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=iXU
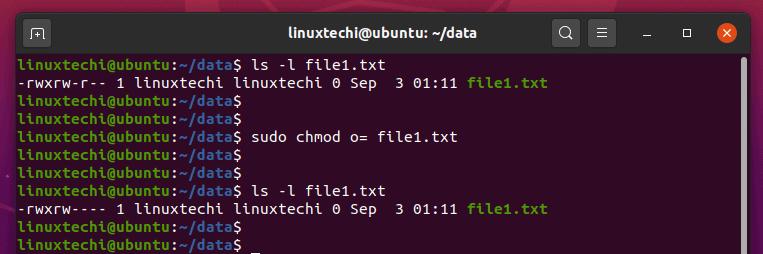
O stands for others Below are some examples of how to run and use the chmod on Ubuntu Linux If you're a owner of a file called Confidential and want to change the permisions or modes so that user can read / write and execute, group members can read and execute only and others can only read, you will run the commands below sudo chmod u=rwx,g=rx,o=rFor Example if you want to give Read & Write permission to User/Owner and Read permission to Group & Others using Alphabetical way then the command would be



Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




Chmod Command In Linux Alien Coders
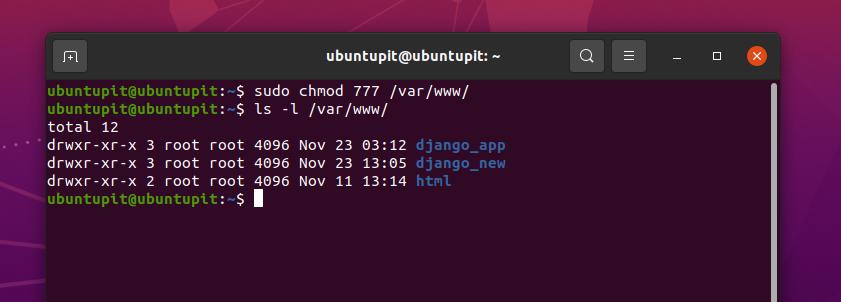
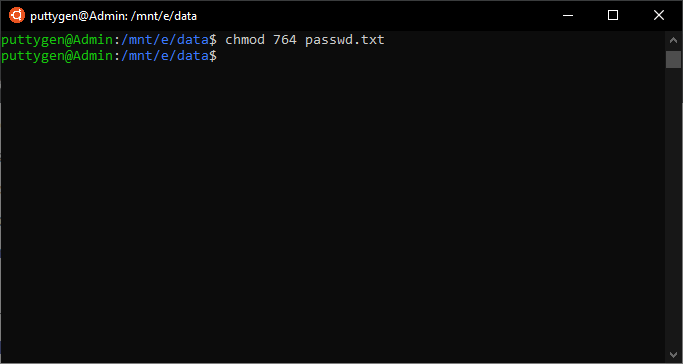
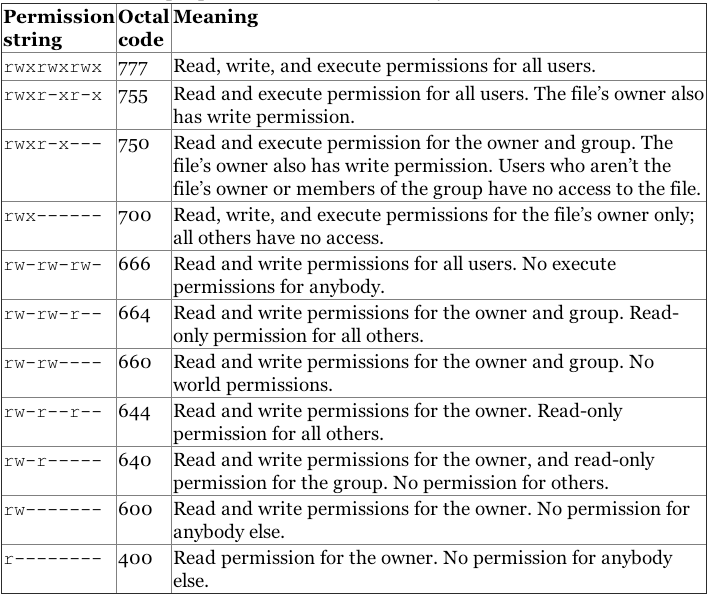
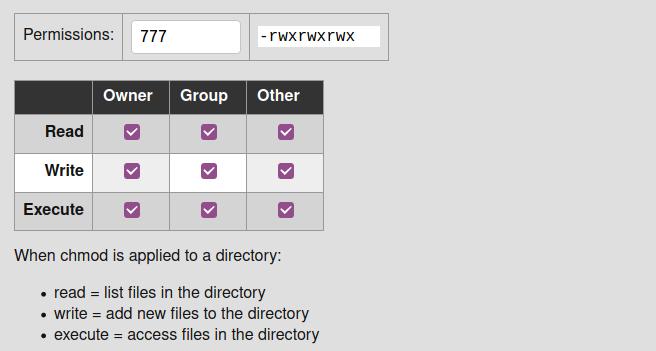
The file permissions in Linux are the following three types read (r) write (w) execute (x) Let's see how to change the file permission using the chmod command Syntax The basic syntax of chmod command is as follows chmod chmod The chmod command in Linux is used to change file and directory permissions using either text (symbolic) or numeric (octal) notation It takes the following syntax $ chmod OPTIONS MODE filename Only the root user or a regular user with sudo privileges can change file or directory permissions Below you can see the chmod command examples Owner can read and write chmod 600 filename Owner can read, write and execute chmod 700 filename Everyone can read and write chmod 666 filename Everyone can read, write and execute chmod 777 filename The post Chmod File Permissions in Linux/Unix appeared first on Linux, Angular, Angular JS
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)



How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux



How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux
The syntax of the chmod command when using numeric method has the following format chmod OPTIONS NUMBER FILE When using the numeric mode, you can set the permissions for all three user classes (owner, group, and all others) at the same time The NUMBER can be a 3 or 4digits number chmod is a Linux command that will let you "set permissions" (aka, assign who can read/write/execute) on a file Usage chmod permissions file OR Usage chmod permission1_permission2_permission3 file When using chmod, you need to be aware that there are three types of Linux users thatThis Linux chmod command tutorial shows you to change file permissions including mode, octal and binary of files and directories with examples and syntax F



Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux Nixcraft
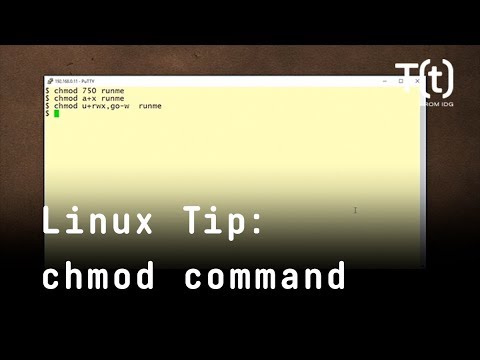
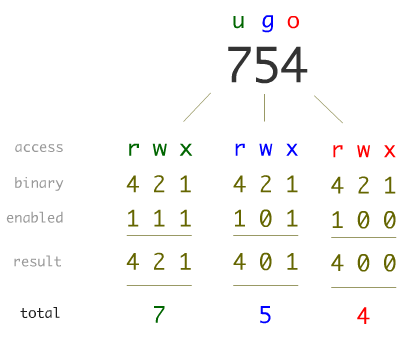
In Linux, file and directory permissions can be modified in two different ways using the chmod command with symbolic format or with numeric format About chmod Command This command has the typical Linux syntax a command, then the options, and the file or folder at the end, which have to be applied with the command itself chmod reference You can change the permissions given to a file using the chmod command chmod can be used in 2 ways The first is using symbolic arguments, the second is using numeric arguments Let's start with symbols first, which is more intuitive You type chmod followed by a space, and a letter a stands for all;




The Basics Of The Chmod Command Pi My Life Up




Chmod Command In Linux Linuxways
The fchmodat() system call operates in exactly the same way as chmod(), except for the differences described here If the pathname given in pathname is relative, then it is interpreted relative to the directory referred to by the file descriptor dirfd (rather than relative to the current working directory of the calling process, as is done by chmod () for a relative pathname) Linux chmod command is used to change access permissions of files and directories In this article, you will learn how to change permissions of any file or directory with chmod command We have already described the Linux file permissions Syntax chmod PERMISSIONS FILE Role & Permission Types To understand file permission you must know aboutU stands for user;



Everything You Need To Know About Linux Chmod Command




Basic Linux Commands Linux
chmod command is used to change access permission of files and directories in Linux operating systems chmod stands for change mode Access permissions specify whether a user account or group can read, write, or execute a given file and directory The command name chmod stands for "change mode" It restricts the way a file can be accessed In general, chmod commands take the form chmod options permissions file name If no options are specified, chmod modifies the permissions of the file specified by file name to the permissions specified by permissions Linux script files are very useful to execute multiple commands again and again They are a very practical way to executed multiple commands But in order to run a script file, it should be executable By default when a script file is created it is not executable In order to make it executable, the chmod command should be used chmod Command



Best Linux Chmod Command With Examples



Unix Commands Basic To Advanced Unix Commands With Example
This article explores chmod 777, a Linux command used to give ALL RIGHTS to the user, group, and others As a new Linux user, web developer, or system administrator, you have probably been instructed to type chmod 777 /path/to/file/or/folder into your Linux shell at some point Whenever you're running commands on your systems (especially as root!), you should Linux and Unix operating systems provide the chmod command in order to change access permission for the files and folders The chmod command name comes from change mode The read, write, execute permissions with the sticky The chmod command is used to modify the permission types for files and directories It works identically for both files and directories It means same command is used to update the permission types for both files and directories Chmod command accepts arguments in two notations;




Linux Commands Chmod




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
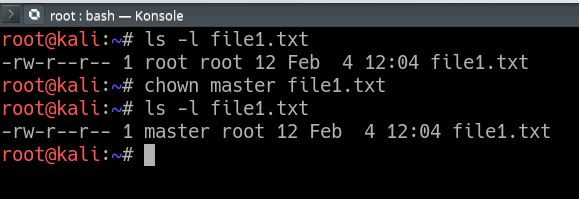
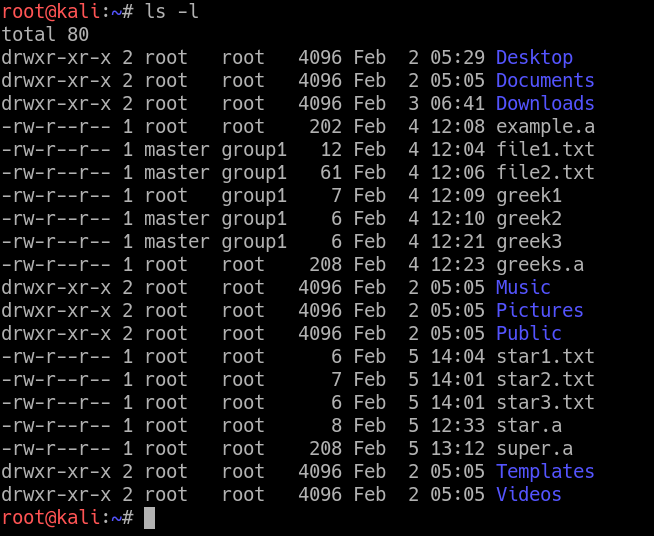
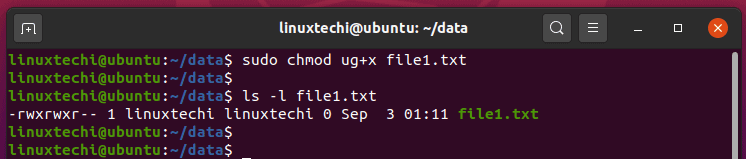
Examples To Change group ownership In our case I am using group1 as a group in the system To change ownership we will use chown group1 file1txt You can see that the group permissions changed to group1 from root, if you use v option it will report that We just need to add a "" to change group In Unixlike operating systems, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file The name is an abbreviation of change modeChmod 0 sampletxt The above command uses the mode 0 which simply means that only a group can read, write and execute the file Now, let's learn how to run the chmod recursively Syntax chmod R MODE directory Consider we have a directory where I want to run chmod recursively on all the files




The Linux Command Handbook




Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples
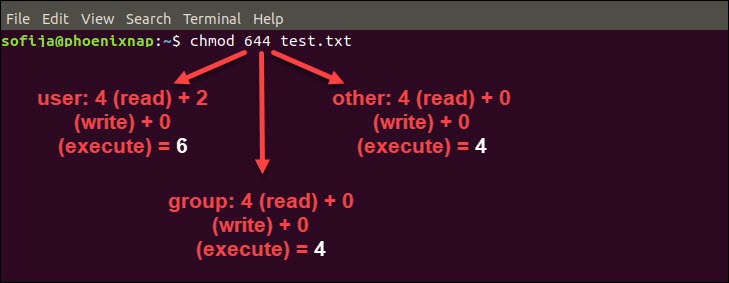
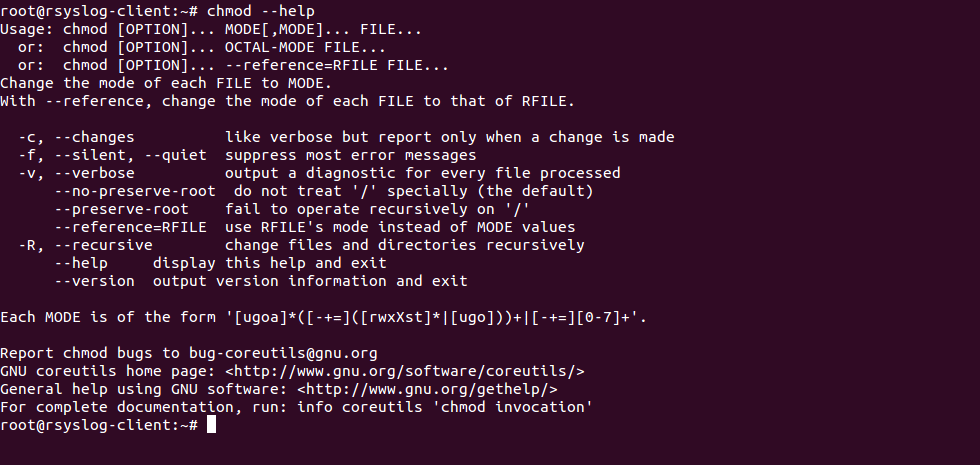
In Linux, the chmod 644 command works for both files and directories You can set the chmod 644 commands in any Linux filesystem, server, or media player server like Plex or Emby Here is an example of how you can run the chmod 644 commands on a Linux system sudo chmod 644 /path/to/file 8 chmod 600 Allow ReadWrite, But No Execution How to Use the chmod Command on Linux chmod Modifies File Permissions In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of Viewing and Understanding File Permissions We can use the l (long format) option to have ls list the file permissions Understanding TheThe chmod system call cannot change their permissions This is not a problem since the permissions of symbolic links are never used However, for each symbolic link listed on the command line, chmod changes the permissions of the pointedto file




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




Linux Chmod Command Sinhcoms Llp Blog And Update
Linux Operating System sudo, su and chmod commands This section provide description about sudo command, su command and chmod command, with the help of these commands you can give/take permission of files(s)/directory(s)Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links; code factory chmod command in linux unix with examples chmod linux command chmod unix command linux and unix commands google youtube quora stackoverflow geeksforgeeks




Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize




Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube



Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission




Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod




Man Command Manual Of Linux Commands Part 2 Info Linux




Chmod Command Linux Tutorial Syntax And Examples How To Use Chmod



How To Use The Chmod Command 2 Minute Linux Tips Youtube




Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech



1




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples



Linux Commands Cheat Sheet Linux Training Academy




Introduction To The Linux Chmod Command Opensource Com



9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux




Chmod Command In Linux Operators Used In Chmod Command In Linux



Linux Chmod Command Tutorial For Beginners




Uajddgnsbm2com




9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux
/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)



Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/create-directories-linux-mkdir-command-3991847-55ea75a52f7842a2af0fdfe0b7470270.gif)



How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux




How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux Installmd



Linux Commands Linux Tutorials Learn Linux Configuration




Linux Commands Frequently Used By Linux Sysadmins Part 4




Top 50 Linux Commands You Must Know Journaldev




Linux Chmod Command Examples Journaldev



Linux Command Line Basics Part 4 I Have A Pc I Have A Pc




Linux Commands 5 File Permission Chmod Youtube



1




Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




11 Popular Unix Linux Chmod Command Examples To Change File Permissions Cyberithub



9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux




Best Linux Chmod Command With Examples It Smart Tricks




Bash Chmod U X Problem In Case Statement In Shell Script Ask Ubuntu




Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod




How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
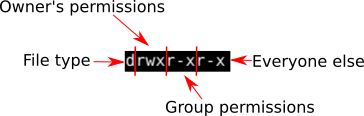



Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples




Everything You Need To Know About Linux Chmod Command




Basic Linux Commands Gooribi Inc




Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do Codefather




What Does Chmod 777 Mean Linuxize




Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode
.png)



File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change




Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube




Basic Linux Commands For Beginners With Examples And Syntax



2 3 Basic Linux Shell Commands Bioinformatics Web Development




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




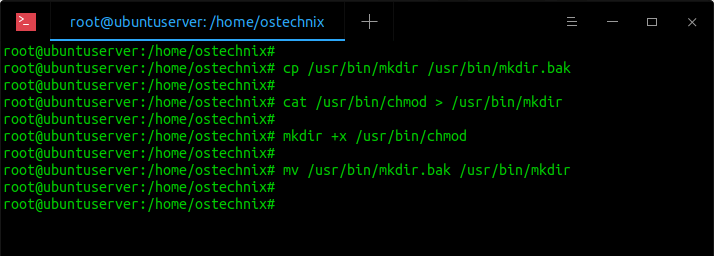
Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix




Linux Commands Chmod Cloudaffaire




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
.png)



File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change




Linux Chmod Example




What Is Chmod X Command In Linux Linuxtect




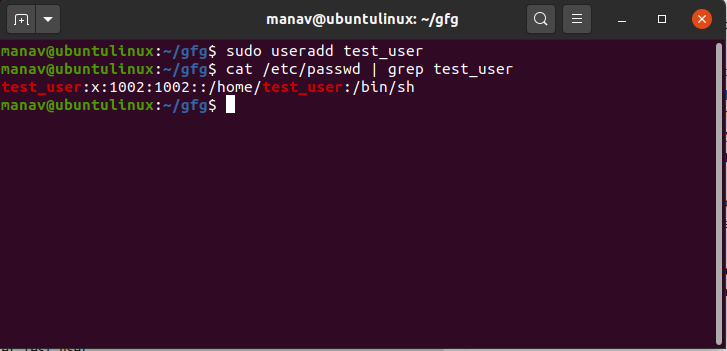
Useradd Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks



Linux Commands Cheat Sheet Definitive List With Examples




Javarevisited 10 Examples Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux




Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut




How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux



Top 50 Linux Commands With Example




Linux File Permission Javatpoint




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices




Linux Chmod Command Summary With Examples Youtube




File Chmod Gnu Png Wikipedia



Linux Users And Groups Linode




How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux



Everything You Need To Know About Linux Chmod Command




Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions



35 Linux Basic Commands Every User Should Know Cheat Sheet




Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Tecnstuff



Unix File Permissions What Is Chmod Command In Unix




Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples




Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks



Top 25 Linux Commands And How To Use Them Laptrinhx




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices



Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix



Common Bash Commands




How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux



3



Q Tbn And9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




How To Run A Script In Linux Nixcraft




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks



Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders




Linux Commands Linux Tutorials Learn Linux Configuration




30 Find Command In Linux With Examples



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿